How to purvey and store raw materials for substrates
Raw materials for oyster mushroom substrates
How to purvey and store materials.
- If you work with straw, then it is better to harvest it right away for the whole season, and from one – three fields in one farm. In summer, the humidity of the straw is the lowest – therefore, you will pay for the product, not for the moisture it contains. And “off the field” the price is cheaper.
It is desirable to agree about the deal in advance. You should purchase a product from good farms, where farmers perform:
crop rotation,
foliar fertilizing of cereals
soil fertilization.

During mowing and haymaking time, it is necessary to collect the straw for nitrogen analysis. Then select the field where the nitrogen indicator is the highest and buy the hay bales from this field.
If there is no opportunity to purchase raw materials for the whole season or there is no place to store, it is advisable to buy it from the same farmer or on the farm, where the bales are stored in the covered hangars.
- If you buy straw in the winter from the haystacks stored outdoors, then you need to cut several bales to make sure that the stems inside are not rotten or fusty. Or push some of the straw aside in the bale with the edge of your palm, determine the presence of musty odor, and try to pull some of the stems from the inside of the bale with an iron hook. Moldy, watersoaked bales should be avoided by all means. You should not buy them, even at a very cheap price.
If you risked and bought such a bale – then make sure to discard the most damaged areas of it before processing and increase processing time – at least by half.
- Husks need to be purchased every two to three months, storing it longer is dangerous – it absorbs moisture very well. If you buy for a longer period – store it in a dry room and move it at least once a month from place to place. It is possible to mix the hull with straw, it is stored much better this way. Long-stored husks need to be sieved to remove mouse and rat excrements from it – the husk tend to stick and form mold around them.
Do I need to chop the straw?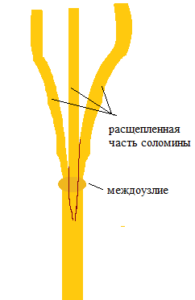
(Междоузлия-Internodes
Разделенная часть соломы-
Split part of straw)
The springiness and creasing property of straw from almost all cereals is sufficient to make it a base for good substrate even without further grinding. It is much more important to split the hollow stalk of the straw (rather than to grind it), so that there are no hollow tubes left and to break the internodes.

Straw chopper in operation.
The springiness and creasing property of straw from almost all cereals is sufficient to make it a base for good substrate even without further grinding. It is much more important to split the hollow stalk of the straw (rather than to grind it), so that there are no hollow tubes left and to break the internodes.
For this purpose, heavy tractors will fit – they squeeze and split the straw with their weight. If there is no tractor, you can chop it. There are many varieties of straw choppers, you need to choose one that does not crush or grind straw but rather briuises or cuts the straw along.
This type of straw cutter also scratches off a wax layer on the outside of the stem. This is especially important for barley straw in arid years. If you make a substrate from such a straw without flattening or bruising it, then the yield will be extremely low. This is because the mycelium will not be able to disentangle the raw material components because of the wax coating.
